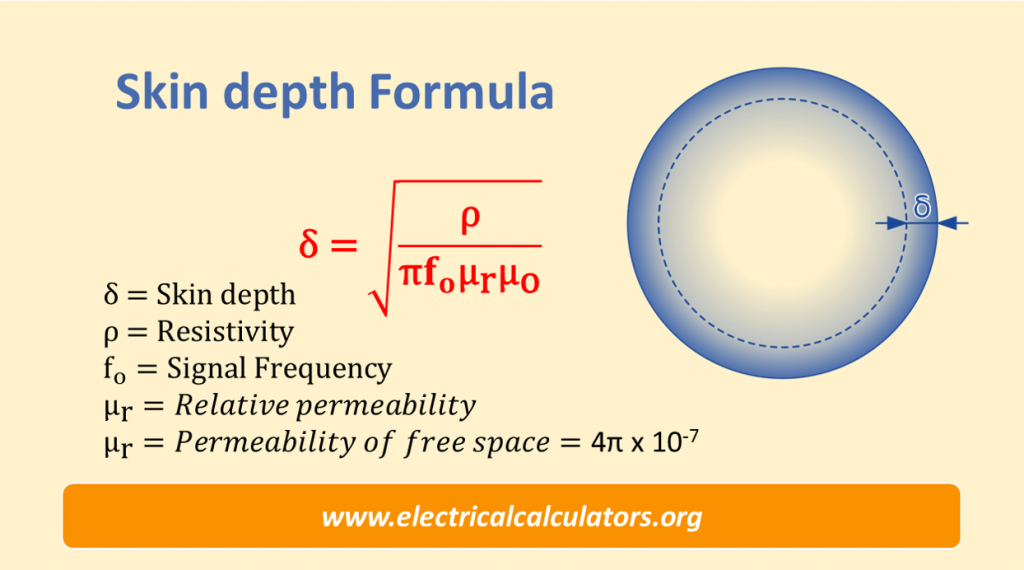
Skin depth formula calculate is used to calculate skin depth from known values of resistivity, relative permeability, and frequency.
- In case of Copper: Resistivity ρ = 1.678 μΩ cm, Relative permeability μr = 1 is used
- In case of Aluminum: Resistivity ρ = 2.6548 μΩ cm, Relative permeability μr = 1.00002 is used
- In case of Gold: Resistivity ρ = 2.24 μΩ cm, Relative permeability μr = 1 is used
- In case of Silver: Resistivity ρ = 1.586 μΩ cm, Relative permeability μr = 0.998 is used
- In case of Nickel: Resistivity ρ = 6.84 μΩ cm, Relative permeability μr = 600 is used
Skin Depth Formula Equation
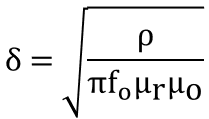
- δ = skin depth
- ρ = resistivity
- fo = signal frequency
- μr = relative permeability
- μo = permeability of free space = 4π x 10-7
What is Skin Depth
The term skin depth is linked with the skin effect, which itself is related to the field of Electrical Engineering and Electromagnetism. Skin effect is defined as the capability of an alternating electric current (AC) to become distributed within a conductor in such a way that the current density is the largest near the surface of the conductor and decreases exponentially with greater depths in the conductor. Electric current flows primarily at the “skin” of the conductor, between the outer surface and a level called the skin depth. The calculation of skin depth requires frequency of AC signal, resistivity and relative permeability of the conductive material.
Technically, the skin depth, δ, is defined as the depth where the current density is around 1/e (about 37%) of the value at the surface. The skin depth depends on the frequency of the current and the electrical and magnetic properties of the conductor.